| Topics | SPM’s Key Responsibilities |
| **Ideation** | Work with the business to identify and build an Ideas/Initiatives backlog Own and oversee one or multiple initiatives Create Opportunity Canvas Identify key opportunities and problems Mapping Ideas/Initiatives to Business Objectives (OKRs), Mission and Vision Prioritise Ideas/Initiatives Create and prioritise Assumptions |
| Discovery | Work with User Research and Service Design through data insight and user research studies to Find, collate and extract key customer insights Articulate the problem space into discrete problem statements Identify target users and their pain points Prioritise users, their problems and pain points **Define Experiments** Work with Service Design, UX and Tech leads on potential solutions addressing the user problems and pain points Create and prioritise Assumptions Create and prioritise Hypotheses Identify and define the metrics to capture and support the hypotheses and test cards Create and prioritise Test Cards Compile **Business Case** to fund agreed delivery scope and confirm financial sustainability |
| Validation through Experimentation | Build backlog of Epics (including the hypotheses) to conduct initial experiments Define the minimum viable solution/product to enable the hypotheses to be tested Capture learnings and review hypothesis Assess if problem solution fit has been achieved Work with Architects to assess technical feasibility on solutions/products proved by the hypotheses in order to build in scale |
| Value Proposition Design (Product Definition) | Define the product (The What), users (The Who), and the benefits (The Why) linked to the business mission and vision Define the Product definition through Value Proposition Design by working on The WHO = User targets The WHY Their jobs to be done (JTBD) Their Needs Their Problem Their Benefits (gains) The WHAT = Potential solutions that fits the problems Scope KPIs (north star metrics to capture and track) Define and drive the Product Vision and Strategy linking to the WHO WHAT WHY Business OKRs, Mission and Vision Build, own and maintain outcome based Product Roadmap linked to relevant OKRs Build and prioritise **backlog of Epics and Features** and liaise with PM who will create user stories Work with Architecture or Tech leads to conduct feasibility assessment of the features |
| Horizon and Release Plan | Define MVP and major releases including the scope Plan the upcoming horizons (90/180 days) and communicate to PMs so they can align their sprint planning with the Horizon and Release plans |
| **Stakeholder Management** | This is the core part of the Product Management job and require great deal of good soft skills particularly building empathy with stakeholder, challenge them with evidence, and get their buy-in.
Build empathy and a strong and strategic relationship with Senior stakeholders such as Business Owners, Product Council, and the customer(s) to align on the value proposition
Challenge stakeholders with evidence to protect the scope of the Product (Say No by not say No - soft skills come here )
🙂 |
| Landscape Analysis (Market, Competitors, Trends, Technology) | Identify and analyse Market landscape Competitors Trends Technologies and Solutions Potential Partners Build vs Buy |
| Scrum Ceremonies | Daily Scrum: Generally optional for SPM to attend unless he/she is involved in some tasks in a sprint Sprint Review: Attend and see the work done by the team and provide input/feedback Invite and encourage Senior Stakeholders to attend the review session (inform the PM if SLT or the customer will be attending) Sprint Planning Generally optional to attend when there is a SPM and PM set up but that can adapt when SPM is also involved in conducting planned work for the next sprint being planned. But the session is led by the PM Sprint Retrospective: attend and participate as scrum team member |
| Topics | PM’s Key Responsibilities |
| Validation and Experimentation | Maintain and refine the backlog with user stories based on the Epics and hypotheses created by SPM Prioritise stories based on the release and horizon plan created by SPM |
| Stakeholder Management | This is the core part of the Product Management job and require great deal of good soft skills particularly building empathy with stakeholder, challenge them with evidence, and get their buy-in.
Build empathy and a strong relationship with the following roles/ disciplines and maintain the line of communication with them
Product Manager
Engineering
Service Design
UX Design
The end user (customer)
Business (e.g. service lines)
Challenge your stakeholders with evidence to protect the scope of the Backlog (Say No by not say No - soft skills come here )
|
| Backlog Management | Create user stories Develop acceptance criteria Prioritise user stories Define metrics to support KPIs Backlog Refinement: Refine stories and acceptance criteria with UR, UX Design and Engineering split and slice the stories so they can be delivered in one sprint - following the INVEST model (stories shall be Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Small and Testable) Maintain backlog hygiene Work with the scrum team to refine stories (take their inputs, analyse and incorporate to the stories considering the sprint goals and size of the stories - Say no when their inputs are not aligned with the sprint goals or increases the size of the story) provide a rough estimate on stories prior to Sprint Planning ensure user stories meet the Definition of Ready |
| Sprint Management | Build sprints backlog Set Sprint goals in line with the Release and Horizon plans that SPM provides and agree the Sprint goals with SPM Communicate the Sprint goals to the scrum team Review the work at the end of the sprint and check against the acceptance criteria On completion of stories, PM assesses the stories against acceptance criteria and DoD and close the stories once DoD is met Support the Delivery Manager / Scrum Master to Remove Impediments Work with the Delivery Manager / Scrum Master to Create, Apply and improve Definition of Done |
| Scrum Ceremonies | Daily Scrum: Support the team if there is a blocker that concerns the Product Track the progress Remind the sprint goals to the scrum team Sprint Review: Review the Sprint Goals with the team Review the work from the team and check against a/c (acceptance criteria) Accept a work as done or incomplete Sprint Planning Lead the sprint planning Communicate the Sprint Goals Review the agreed stories and a/c with the team Lead the estimation with the team Decide which stories can be moved to the backlog when the velocity is reached. Sprint Retrospective: attend and participate as scrum team member |
| Topics | Shared responsibilities |
| Risk Management | Delivery Manager … Capture, prioritise and track risks, constraints, challenges and issues and communicate with the SPM/PM |
| Analytics | Review and measure KPIs and Metrics Data analysis Capture and analyse user feedback |
| **Release Plan** | Planning the releases Production Release Roll out Customer / User readiness support comms |
| Stakeholder Management | As stated in the above sections for both SPM and PM |
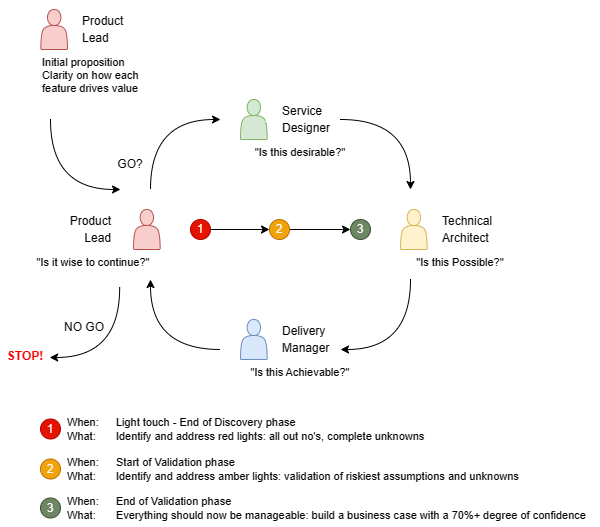
At the back end of discovery we should ask the following questions to increase confidence in the business case. These questions should be part of a collaborative conversation in thee amigos style.
[](https://pirate.cooking/uploads/images/gallery/2023-09/oYbimage.png) 1. **Validation with Technical Architect** - Have you discussed the product goal and solution approach with a technical architect? - Has the technical architect deemed the approach both technically feasible and financially viable? 2. **Confidence in Solution Delivery** - Do you have a high level of confidence that you can deliver a solution that effectively meets the value proposition? On what basis? - Have there been any prototypes or POCs (proof of concepts) created to validate your confidence? 3. **Trade-offs and Value Delivery** - Can you outline potential trade-offs or decision-making scenarios you anticipate during the development phase? - How do you plan to prioritize features to ensure timely value delivery? 4. **Assumptions on Scalability and Longevity** - What are your projections for scalability? How do you foresee the product/service scaling over time? - Have you considered how technology or market changes may impact the longevity of your current approach? 5. **Non-functional Requirements** - Are there specific non-functional requirements you've identified, such as data volume, service uptime, performance metrics, or security protocols? - How did you come to these non-functional requirements, and how critical are they to the product's success? 6. **Critical Components vs. Flexible Components** - Which components of the product/solution are non-negotiable and critical for launch? - What elements do you foresee being able to change or iterate upon post-launch based on user feedback or market dynamics? 7. **Consumer Identification and Targeting** - How have you identified and segmented the potential consumers of the service? - What strategies or channels are you using to reach and deliver value to these consumers? 8. **Operational Costs and Outsourcing** - How have you calculated the operational costs associated with this solution, and what is the projected impact on the business's bottom line? - If there's a need to outsource specific skills or services, how does this affect the business case? Have you compared the costs of insourcing versus outsourcing? 9. **Technical Dependencies and Integrations** - Are there any third-party services or platforms on which your solution is dependent? - Have you considered potential risks or challenges with these integrations, and do you have a mitigation plan? # Templates # Value Proposition Canvas| **Value Proposition Canvas - TEMPLATE** | |
| **Context & Background** | |
| **Problem Magnitude ** in volumes and £ | |
| **Target Audience & Jobs To Be Done** | |
| **Key Needs & Pain Points** Primary Needs: Primary Pain points: | |
| **Value Proposition Statements** {Product X} helps {primary users} to (Primary jobs to be done) by reducing (Key pains), and by delivering (Key gains) {Product X} helps {Secondary users} to (Primary jobs to be done) by minimising the (Key pains) and by (Key gains) | |
| **Vision Statement** | |
| **Scope & Priorities** | |
| **Approach** | |
| **Strategic Objectives / Measurable Outcomes** | |
| **Delivery Channel** | **Metrics** |
| **Opportunity** | **Landscape / Competitors** |
| **Assumptions & Unknowns** | |
| **Cost** | |
This template can be used to document Experimentations, PoCs, PoVs and Technology Evaluation activities. The template is dynamic and some parts of it can change based on the context and nature of the experiment.
| ##### Experimentation Canvas {the name of the experiment} | |
| The Context (A brief description of the background work) text | |
| The Opportunity / Problem (A brief statement of the problem that leads to the need for running an experiment in the form of PoC or PoV or Tech evaluation) text | |
| The Experiment (A brief description of what the experiment is about and if there is a 3rd party involved ) text | |
| The Hypotheses (What we believe that can tackle the problem or augment the opportunity) We believe … | |
| The Scope (What do we want to experiment? Clearly specify the scope of the experiment both from Product and Tech perspectives) | |
| The Use Cases (Specify the use cases in scope for the experiment) | |
| The Objectives (Specify the objectives from Product and Tech perspectives) Product Technology | |
| Risks, Dependencies, Constraints (Specify any potential risks, constraints or dependencies and a mitigation plan) | |
| Key Metrics to Capture (Specify the key metrics we want to capture to support the hypotheses) | Success Criteria and Outcome (Specify the use cases in scope for the experiment) |
| Technology Assessment Checklist (The criteria for assessing a new technology and its integration to the existing systems) Accuracy Security Ease of Integration Any other criteria | Key Resources (Resources, Skillsets and capabilities required to conduct the experiment) |
| Prerequisites and Sprint 0 (List all prior activities required to be done before the experiment can start, e.g. Data, Dev Environment etc) | Key Stakeholders (Sponsors, 3rd parties, business owner etc) |
| The Cost (A blink estimate cost of running the experiment - can be removed if it should not be disclosed) | Useful Sources (Links to any knowledge base or source relevant to experiment ) |
